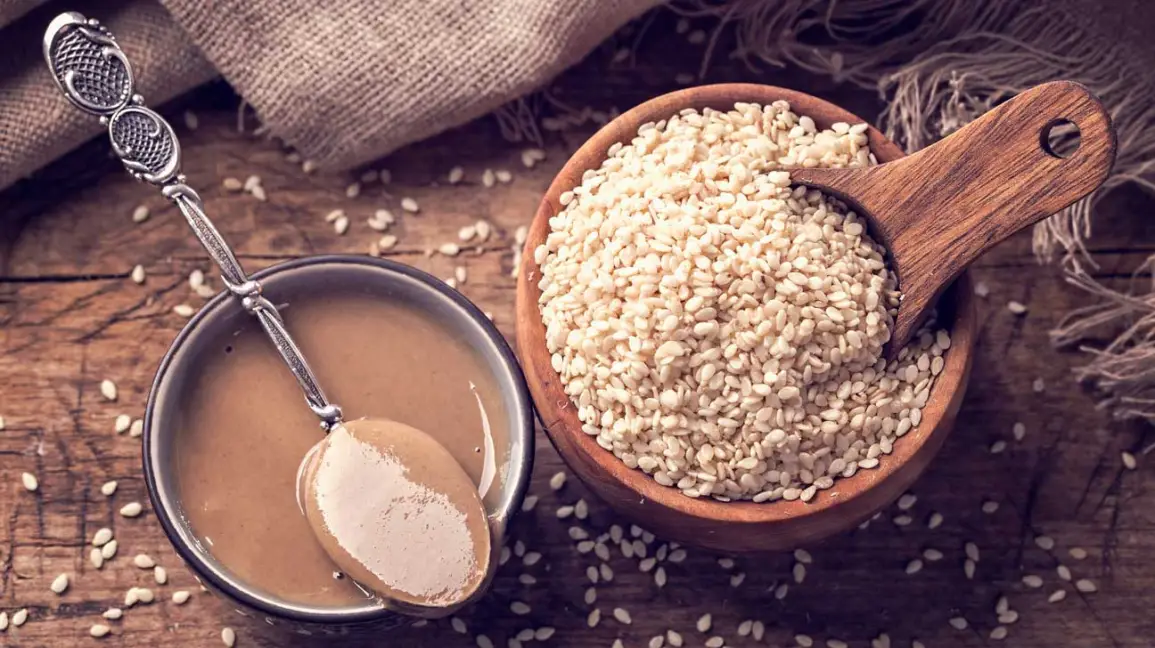
Tahini, a creamy paste made from ground sesame seeds, has been a staple in Middle Eastern, Mediterranean, and North African cuisines for centuries. This versatile ingredient is much more than just a key component of hummus; it’s a nutritious, flavorful addition to countless dishes around the world. From its ancient origins to its modern-day popularity, tahini has earned its place as a beloved pantry essential in homes and restaurants alike. In this article, we’ll explore the history, nutritional benefits, uses, and recipes that make tah ini a unique and indispensable ingredient.
A Brief History of Tahini
The roots of tahini trace back thousands of years to the ancient civilizations of Mesopotamia and Egypt. The earliest recorded mention of sesame seeds, and by extension tahini, dates back to 2500 BCE. In fact, the earliest known recipe for tahini-like pastes comes from the ancient Assyrians, who used sesame seeds in their culinary practices. Over time, the sesame seed spread throughout the Middle East and into the Mediterranean region.
In the Middle Ages, the Islamic Golden Age saw further refinement of sesame-based products, including tahini, which became integral to the region’s cuisine. Ancient Egyptians made use of sesame oil and seeds, and it is believed that they were one of the first to develop tah ini as we know it today. By the 20th century, tahini had become a popular ingredient throughout the Middle East and North Africa. It gained international recognition as global culinary tastes began to expand and interconnect.
In modern times, tahini is not only used in traditional dishes but has also found its way into more contemporary recipes across the globe. Its health benefits, creamy texture, and rich flavor make it a go-to ingredient for both savory and sweet dishes.
How Tahini is Made
Tahini is made by grinding roasted or raw sesame seeds into a smooth, oily paste. The process of making tahini typically involves either cold-pressing or dry-roasting sesame seeds, which releases the oil and makes the seeds easier to blend. Depending on whether the seeds are roasted or raw, the resulting tahini can have a slightly different flavor profile: roasted sesame seeds lend a deeper, nuttier taste, while raw seeds offer a more delicate, earthy flavor.
In its purest form, tahini consists solely of ground sesame seeds. However, it is also common to find tahini products that have been enhanced with ingredients like salt, lemon juice, olive oil, or garlic to create a more complex flavor. Tahini’s consistency can vary from thick and paste-like to a more liquid texture, depending on the brand or specific recipe.
Nutritional Benefits of Tahini
One of the reasons tahini has gained such widespread acclaim is its impressive nutritional profile. It is a highly nutritious food packed with vitamins, minerals, healthy fats, and plant-based protein. Here are some of the standout health benefits of tahini:
1. Rich in Healthy Fats
Tahini is an excellent source of unsaturated fats, particularly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health. These healthy fats help reduce bad cholesterol levels, lower the risk of heart disease, and promote overall cardiovascular health.
2. A Good Source of Protein
For plant-based eaters, tahini serves as an important protein source. A tablespoon of tah ini contains around 2–3 grams of protein, which is valuable for muscle building, immune function, and overall bodily repair.
3. Packed with Minerals
Tahini is especially high in minerals like calcium, magnesium, and iron. The calcium content makes it a great addition to a plant-based diet for supporting bone health. Magnesium plays a key role in muscle function and regulating blood sugar levels, while iron is essential for the formation of red blood cells and overall energy levels.
4. High in Fiber
Sesame seeds contain a healthy amount of fiber, which is beneficial for digestive health. Fiber helps regulate bowel movements, reduces the risk of constipation, and may contribute to better weight management by promoting satiety.
5. Rich in Antioxidants
Tahini also contains antioxidants such as sesamin and sesamolin, which are compounds found in sesame seeds that help protect cells from oxidative damage. These antioxidants may help reduce inflammation and support long-term health.
6. Vegan and Gluten-Free
As a naturally vegan and gluten-free food, tah ini is an excellent ingredient for people following specific dietary restrictions or preferences.
Uses of Tahini in Cooking
Tahini’s versatility as an ingredient is one of the key reasons it has gained such widespread popularity. Whether used as a dressing, dip, spread, or even in baked goods, tah ini can enhance the flavor and texture of a wide variety of dishes. Here are just a few of the many ways tah ini is used in cooking:
1. Hummus
The most famous use of tah ini is in hummus, the creamy chickpea-based dip that is a staple in Middle Eastern cuisine. Tah ini is blended with chickpeas, olive oil, garlic, lemon juice, and salt to create a smooth, velvety dip that pairs perfectly with pita bread, vegetables, or crackers.
2. Salad Dressings and Sauces
Tahini makes an excellent base for salad dressings and sauces. By thinning it with lemon juice, garlic, and a bit of water, you can create a tangy, creamy dressing that’s perfect for drizzling over fresh vegetables, grains, or roasted meats. Tah ini-based sauces also pair wonderfully with grilled meats like chicken and lamb.
3. Baking
Though not as commonly associated with desserts, tah ini can be used in baking for a rich, nutty flavor. It can be incorporated into cookies, cakes, and brownies, providing a depth of flavor that complements chocolate, fruit, and spices. One popular example is tah ini cookies, where the paste adds a luscious texture to the dough.
4. Smoothies and Shakes
Tahini can also be used in smoothies and protein shakes, adding both creaminess and nutritional value. Its rich, nutty flavor complements ingredients like banana, chocolate, and berries, making for a satisfying breakfast or snack.
5. Savory Dishes
In addition to being a component of hummus, tah ini can be used in savory stews, soups, and roasted vegetable dishes. It can be stirred into soups for added creaminess or drizzled over roasted cauliflower, eggplant, or sweet potatoes for an extra burst of flavor.
6. Vegan Substitutes
For those on a vegan diet or looking for plant-based alternatives, tah ini can replace butter or cream in various recipes. It works particularly well as a substitute for cream in pasta dishes, or as a base for vegan “cheese” sauces.
Simple and Delicious Tahini Recipes
Tahini Lemon Dressing
A quick and easy dressing for salads and bowls.
- 3 tablespoons tah ini
- Juice of 1 lemon
- 1 tablespoon olive oil
- 1 garlic clove, minced
- Water to thin (about 2 tablespoons)
- Salt and pepper to taste
Whisk all ingredients together until smooth. Adjust consistency with water, and season with salt and pepper to taste.
Tahini Chocolate Chip Cookies
A nutty twist on the classic chocolate chip cookie.
- 1 cup tahini
- 1 cup sugar
- 1 teaspoon vanilla extract
- 1 cup chocolate chips
- 2 tablespoons flour (optional, for structure)
Preheat the oven to 350°F (175°C). Mix tah ini, sugar, and vanilla until smooth, fold in chocolate chips, and bake on a parchment-lined sheet for 8-10 minutes.
Conclusion
Tahini is far more than just a traditional Middle Eastern ingredient; it’s a nutrient-packed, versatile paste that can be used in a variety of dishes, both sweet and savory. With its rich history, impressive health benefits, and ability to enhance a wide range of recipes, tahi ni deserves a prominent spot in your kitchen. Whether you use it in classic hummus, drizzle it over roasted vegetables, or incorporate it into a dessert, tah ini brings flavor, texture, and nutrition to your meals. So, the next time you reach for a jar, remember that tah ini is not just a culinary ingredient—it’s a bridge between ancient traditions and modern culinary creativity.

 News3 months ago
News3 months ago
 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months ago
 Tech3 months ago
Tech3 months ago
 Local Information3 months ago
Local Information3 months ago
 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months ago
 Local Information3 months ago
Local Information3 months ago
 Tech3 months ago
Tech3 months ago
 Foods3 months ago
Foods3 months ago